-
why react fast?
virtual DOM + Diffing algorithm
-
Uncontrolled component data acquisition --- Refs
-
string ref (class component)
showData = () => {
const {input1} = this.refs
alert(input1.value)
}
showData2 = () => {
const {input2} = this.refs
alert(input2.value)
}
...
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref="input1" type="text"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>show input1 data</button>
<input ref="input2" onBlur={this.showData2} type="text"/>
</div>
)
}-
callback func ref (class component)
showData = () => {
const {input1} = this
alert(input1.value)
}
render(){
return (
<input ref={c => this.input1 = c} type="text"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>alert data</button>
)
}-
createRef (class component)
myRef = React.createRef()
showData = () => {
alert(this.myRef.current.value);
}
...
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>show data</button>-
lifecycle and related hooks
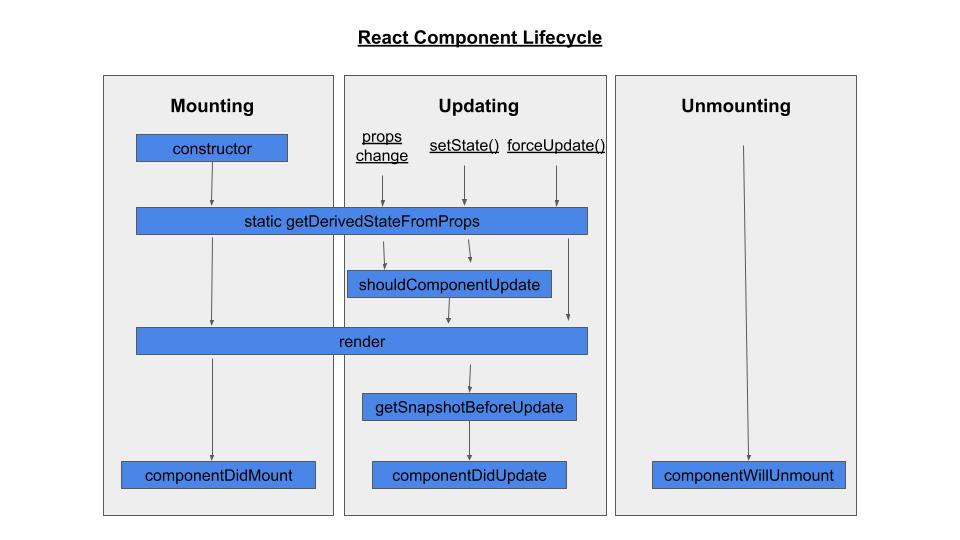
-
components
-
Fragment (<>)
Fragment, often used via <>…</> syntax, lets you group elements without a wrapper node.
<>
<OneChild />
<AnotherChild />
</>-
Profiler
Profiler lets you measure rendering performance of a React tree programmatically.
function onRender(id, phase, actualDuration, baseDuration, startTime, commitTime) {
// Aggregate or log render timings...
}
<Profiler id="App" onRender={onRender}>
<App />
</Profiler>-
StrictMode
StrictMode lets you find common bugs in your components early during development.
<StrictMode>
<App />
</StrictMode>-
Suspense
Suspense lets you display a fallback until its children have finished loading.
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<SomeComponent />
</Suspense>hooks
-
useCallback
useCallback is a React Hook that lets you cache a function definition between re-renders.
const cachedFn = useCallback(fn, dependencies)Parameters: fn: a callback function which is returned by useCallback dependencies: dependencies which fn is relying on. When dependencies changed, a new fn will be returned, otherwise, the same fn will be returned. Usage: Skipping re-rendering of certain component by useCallback and memo
function ProductPage({ productId, referrer, theme }) {
// Tell React to cache your function between re-renders...
const handleSubmit = useCallback((orderDetails) => {
post('/product/' + productId + '/buy', {
referrer,
orderDetails,
});
}, [productId, referrer]); // ...so as long as these dependencies don't change...
return (
<div className={theme}>
{/* ...ShippingForm will receive the same props and can skip re-rendering */}
<ShippingForm onSubmit={handleSubmit} />
</div>
);
}
import { memo } from 'react';
const ShippingForm = memo(function ShippingForm({ onSubmit }) {
// ...
});-
useContext
useContext is a React Hook that lets you read and subscribe to context from your component.
const value = useContext(SomeContext)useContext returns the context value for the calling component. It is determined as the value passed to the closest SomeContext.Provider above the calling component in the tree. If there is no such provider, then the returned value will be the defaultValue you have passed to createContext for that context. The returned value is always up-to-date. React automatically re-renders components that read some context if it changes. 3. #### useDebugValue useDebugValue is a React Hook that lets you add a label to a custom Hook in React DevTools.
useDebugValue(value, format?)-
useDeferredValue
useDeferredValue is a React Hook that lets you defer updating a part of the UI.
const deferredValue = useDeferredValue(value)import { useState, useDeferredValue } from 'react';
function SearchPage() {
const [query, setQuery] = useState('');
const deferredQuery = useDeferredValue(query);
// ...
}when query changed, deferredQuery will be stale value at first, then it will change to new value. So there is a lag existing. Usage: For searching, old results could be kept until new result is ready.
import { Suspense, useState, useDeferredValue } from 'react';
import SearchResults from './SearchResults.js';
export default function App() {
const [query, setQuery] = useState('');
const deferredQuery = useDeferredValue(query);
return (
<>
<label>
Search albums:
<input value={query} onChange={e => setQuery(e.target.value)} />
</label>
<Suspense fallback={<h2>Loading...</h2>}>
<SearchResults query={deferredQuery} />
</Suspense>
</>
);
}5. #### useEffect
useEffect is a React Hook that lets you synchronize a component with an external system.
```javascript
useEffect(setup, dependencies?)Parameters:
-
setup: The function with your Effect’s logic. Your setup function may also optionally return a cleanup function. When your component is first added to the DOM, React will run your setup function. After every re-render with changed dependencies, React will first run the cleanup function (if you provided it) with the old values, and then run your setup function with the new values. After your component is removed from the DOM, React will run your cleanup function one last time.
-
optional dependencies: The list of all reactive values referenced inside of the setup code. Reactive values include props, state, and all the variables and functions declared directly inside your component body. If your linter is configured for React, it will verify that every reactive value is correctly specified as a dependency. The list of dependencies must have a constant number of items and be written inline like [dep1, dep2, dep3]. React will compare each dependency with its previous value using the Object.is comparison. If you omit this argument, your Effect will re-run after every re-render of the component. See the difference between passing an array of dependencies, an empty array, and no dependencies at all.
example:Connecting to an external system
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { createConnection } from './chat.js';
function ChatRoom({ roomId }) {
const [serverUrl, setServerUrl] = useState('https://localhost:1234');
useEffect(() => {
const connection = createConnection(serverUrl, roomId);
connection.connect();
return () => {
connection.disconnect();
};
}, [serverUrl, roomId]);
// ...
}-
useId
useId is a React Hook for generating unique IDs that can be passed to accessibility attributes.
const id = useId()example:
import { useId } from 'react';
function PasswordField() {
const passwordHintId = useId();
// ...
<>
<input type="password" aria-describedby={passwordHintId} />
<p id={passwordHintId}>
</>
-
useImperativeHandle
useImperativeHandle is a React Hook that lets you customize the handle exposed as a ref.
useImperativeHandle(ref, createHandle, dependencies?)example:Exposing a custom ref handle to the parent component
import { forwardRef, useRef, useImperativeHandle } from 'react';
const MyInput = forwardRef(function MyInput(props, ref) {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => {
return {
focus() {
inputRef.current.focus();
},
scrollIntoView() {
inputRef.current.scrollIntoView();
},
};
}, []);
return <input {...props} ref={inputRef} />;
});-
useInsertionEffect
useInsertionEffect is a version of useEffect that fires before any DOM mutations.
useInsertionEffect(setup, dependencies?)example: Only use for CSS-in-JS lib
// Inside your CSS-in-JS library
let isInserted = new Set();
function useCSS(rule) {
useInsertionEffect(() => {
// As explained earlier, we don't recommend runtime injection of <style> tags.
// But if you have to do it, then it's important to do in useInsertionEffect.
if (!isInserted.has(rule)) {
isInserted.add(rule);
document.head.appendChild(getStyleForRule(rule));
}
});
return rule;
}
function Button() {
const className = useCSS('...');
return <div className={className} />;
}-
useLayoutEffect
useLayoutEffect is a version of useEffect that fires before the browser repaints the screen.
useLayoutEffect(setup, dependencies?)example:Measuring layout before the browser repaints the screen
function Tooltip() {
const ref = useRef(null);
const [tooltipHeight, setTooltipHeight] = useState(0); // You don't know real height yet
useLayoutEffect(() => {
const { height } = ref.current.getBoundingClientRect();
setTooltipHeight(height); // Re-render now that you know the real height
}, []);
// ...use tooltipHeight in the rendering logic below...
}-
useMemo
useMemo is a React Hook that lets you cache the result of a calculation between re-renders.
const cachedValue = useMemo(calculateValue, dependencies)example:Skipping expensive recalculations
import { useMemo } from 'react';
function TodoList({ todos, tab, theme }) {
const visibleTodos = useMemo(() => filterTodos(todos, tab), [todos, tab]);
// ...
}-
useReducer
useReducer is a React Hook that lets you add a reducer to your component.
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialArg, init?)example:
import { useReducer } from 'react';
function reducer(state, action) {
if (action.type === 'incremented_age') {
return {
age: state.age + 1
};
}
throw Error('Unknown action.');
}
export default function Counter() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, { age: 42 });
return (
<>
<button onClick={() => {
dispatch({ type: 'incremented_age' })
}}>
Increment age
</button>
<p>Hello! You are {state.age}.</p>
</>
);
}-
useRef
useRef is a React Hook that lets you reference a value that’s not needed for rendering.
const ref = useRef(initialValue)example: manipulating DOM by ref
import { useRef } from 'react';
export default function Form() {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
function handleClick() {
inputRef.current.focus();
}
return (
<>
<input ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Focus the input
</button>
</>
);
}-
useState
useState is a React Hook that lets you add a state variable to your component.
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState)example: Adding state to a component
import { useState } from 'react';
function MyComponent() {
const [age, setAge] = useState(42);
const [name, setName] = useState('Taylor');
// ...-
useSyncExternalStore
useSyncExternalStore is a React Hook that lets you subscribe to an external store.
const snapshot = useSyncExternalStore(subscribe, getSnapshot, getServerSnapshot?)example:
import { useSyncExternalStore } from 'react';
import { todosStore } from './todoStore.js';
export default function TodosApp() {
const todos = useSyncExternalStore(todosStore.subscribe, todosStore.getSnapshot);
return (
<>
<button onClick={() => todosStore.addTodo()}>Add todo</button>
<hr />
<ul>
{todos.map(todo => (
<li key={todo.id}>{todo.text}</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
);
}
// This is an example of a third-party store
// that you might need to integrate with React.
// If your app is fully built with React,
// we recommend using React state instead.
let nextId = 0;
let todos = [{ id: nextId++, text: 'Todo #1' }];
let listeners = [];
export const todosStore = {
addTodo() {
todos = [...todos, { id: nextId++, text: 'Todo #' + nextId }]
emitChange();
},
subscribe(listener) {
listeners = [...listeners, listener];
return () => {
listeners = listeners.filter(l => l !== listener);
};
},
getSnapshot() {
return todos;
}
};
function emitChange() {
for (let listener of listeners) {
listener();
}
}example:Subscribing to a browser API
import { useSyncExternalStore } from 'react';
export default function ChatIndicator() {
const isOnline = useSyncExternalStore(subscribe, getSnapshot);
return <h1>{isOnline ? '✅ Online' : '❌ Disconnected'}</h1>;
}
function getSnapshot() {
return navigator.onLine;
}
function subscribe(callback) {
window.addEventListener('online', callback);
window.addEventListener('offline', callback);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('online', callback);
window.removeEventListener('offline', callback);
};
}-
useTransition
useTransition is a React Hook that lets you update the state without blocking the UI.
const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition()example:Marking a state update as a non-blocking transition
function TabContainer() {
const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition();
const [tab, setTab] = useState('about');
function selectTab(nextTab) {
startTransition(() => {
setTab(nextTab);
});
}
// ...
}-
APIs
-
createContext
createContext lets you create a context that components can provide or read.
const SomeContext = createContext(defaultValue)example:
function App() {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('light');
// ...
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<Page />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}function App() {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('dark');
const [currentUser, setCurrentUser] = useState({ name: 'Taylor' });
// ...
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<AuthContext.Provider value={currentUser}>
<Page />
</AuthContext.Provider>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}-
forwardRef
forwardRef lets your component expose a DOM node to parent component with a ref.
const SomeComponent = forwardRef(render)example: Exposing a DOM node to the parent component
import { forwardRef } from 'react';
const MyInput = forwardRef(function MyInput(props, ref) {
const { label, ...otherProps } = props;
return (
<label>
{label}
<input {...otherProps} ref={ref} />
</label>
);
});This lets the parent Form component access the Input DOM node exposed by MyInput:
function Form() {
const ref = useRef(null);
function handleClick() {
ref.current.focus();
}
return (
<form>
<MyInput label="Enter your name:" ref={ref} />
<button type="button" onClick={handleClick}>
Edit
</button>
</form>
);
}-
lazy
lazy lets you defer loading component’s code until it is rendered for the first time.
const SomeComponent = lazy(load)import { lazy } from 'react';
const MarkdownPreview = lazy(() => import('./MarkdownPreview.js'));-
memo
memo lets you skip re-rendering a component when its props are unchanged.
const MemoizedComponent = memo(SomeComponent,arePropsEqual?)example:
const Greeting = memo(function Greeting({ name }) {
return <h1>Hello, {name}!</h1>;
});
export default Greeting;-
startTransition
startTransition lets you update the state without blocking the UI.
import { startTransition } from 'react';
function TabContainer() {
const [tab, setTab] = useState('about');
function selectTab(nextTab) {
startTransition(() => {
setTab(nextTab);
});
}
// ...
}