Chapter 1 - Overview
Core Concepts of Java
- Simplicity
- Object Oriented Programming
- Distribution
- Robust
- Safety
- 体系结构中立
- 可移植性
- 解释性
- 高性能
- 多线程
- 动态性
Chapter 3 - Java Basic
data type
8 basic data types
int, short, long, byte, float, double, char, boolean
String
- String is immutable
- Create long String with append - StringBuilder, StringBuffer(multi-thread)
Chapter 4 - Object and Class
Record
- imported in JDK 14 as preview, published in JDK 16
- Immutable, public accessable
record Point(double x, double y) {
public double distanceFromOrigin(){
return Math.hypot(x,y)
}
}Tips on designing class
- Properties should be private
- Do init all properties, instead of relying on default init
- Avoid using too many primitive data types, wrap them as a class intead
- Separate class that has too many responsibilities
- Class name and method name should reflect their responsibility
- Use immutable class if possible
Chapter 5 - Inheritance
Enum
- Enum is a class with limited number of instances.
- Construction method of a Enum is private
Sealed class
- Imported in Java 15 as preview, published in Java 17.
public abstract sealed class MyClass
permits MyChild1, MyChild2 {
}
// In this case, only MyChild1 and MyChild2 can be sub-class of MyClass.
// MyChild1 and MyChild must be either Sealed, Final or Non-sealedTips on designing inheritance structure
- put public method and public attributes in super class
- Avoid using protected
- Use inheritance to achieve “is-a” relationship
- Avoid using inheritance unless it’s meaningful
- Do not change expected behavior when overwriting method
- Use polymophism instead of type check
- Avoid using reflection
Chapter 6 - Interface, lambda experession and inner class
interface
- method in interface are by default public, properteis in interface are by default public static final
- Common functional interface
| Interface | param | return | method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runnable | None | Void | run |
| Supplier | None | T | get |
| Consumer | T | Void | accept |
| BiConsumer<T, U> | T, U | Void | accept |
| Function<T, R> | T | R | apply |
| BiFunction<T, U, R> | T, U | R | apply |
| UnaryOperator | T | T | apply |
| BinaryOperator | T, T | T | apply |
| Predicate | T | boolean | test |
| BiPredicate<T, U> | T, U | boolean | test |
Inner class
- object of inner class always has a reference to outer ojbect, if we don’t want to have this reference, we should use static inner class.
Chapter 7 - Exception, Assersion and log
Exception
- Throwable
- Error
- Exception
- IOException
- Runtime Exception
- Checked Exception: IO Exception, need to be caught and handled.
- Unchecked Exception: doesn’t require catch/handle, i.e. ArrayOutOfBound.
Log
- Level of logs
- SEVERE
- WARNING
- INFO
- CONFIG
- FINE
- FINER
- FINEST
- Update log config: java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=configFile MainClass
Chapter 8 - Generic
Type Erase
In JVM, generic will be created as a class with type param gets erases. For Example, for Pair<T>, it will be Pair<Object>. For Pair<T extends Comparable & Serializable> implements Serializable, it will be Pair<Comparable> implements Serializable.
Limitations of Generic
- Can not use primitive type as type param
- Runtime check only applies to original type. For example, a instance of Pair<String>, this will just check if a is Pair.
- Can not create array with generic type. It will cause issue for the type check.
- Can not use generic in a variable param method. Because it will put param into an array, which will have the issue of previous point.
- Can not instantiate type variable.
- Can not use generic in static method of static field.
- Can not throw or catch instance of generic class.
Inheritance of generic
- No matter S and T have any relationship, Pair<S> and Pair<T> always don’t have any relation.
- To capture inheritance relation, we should use wildcard type. For example, Pair<? extends Employee>
Chapter 9 - Collection
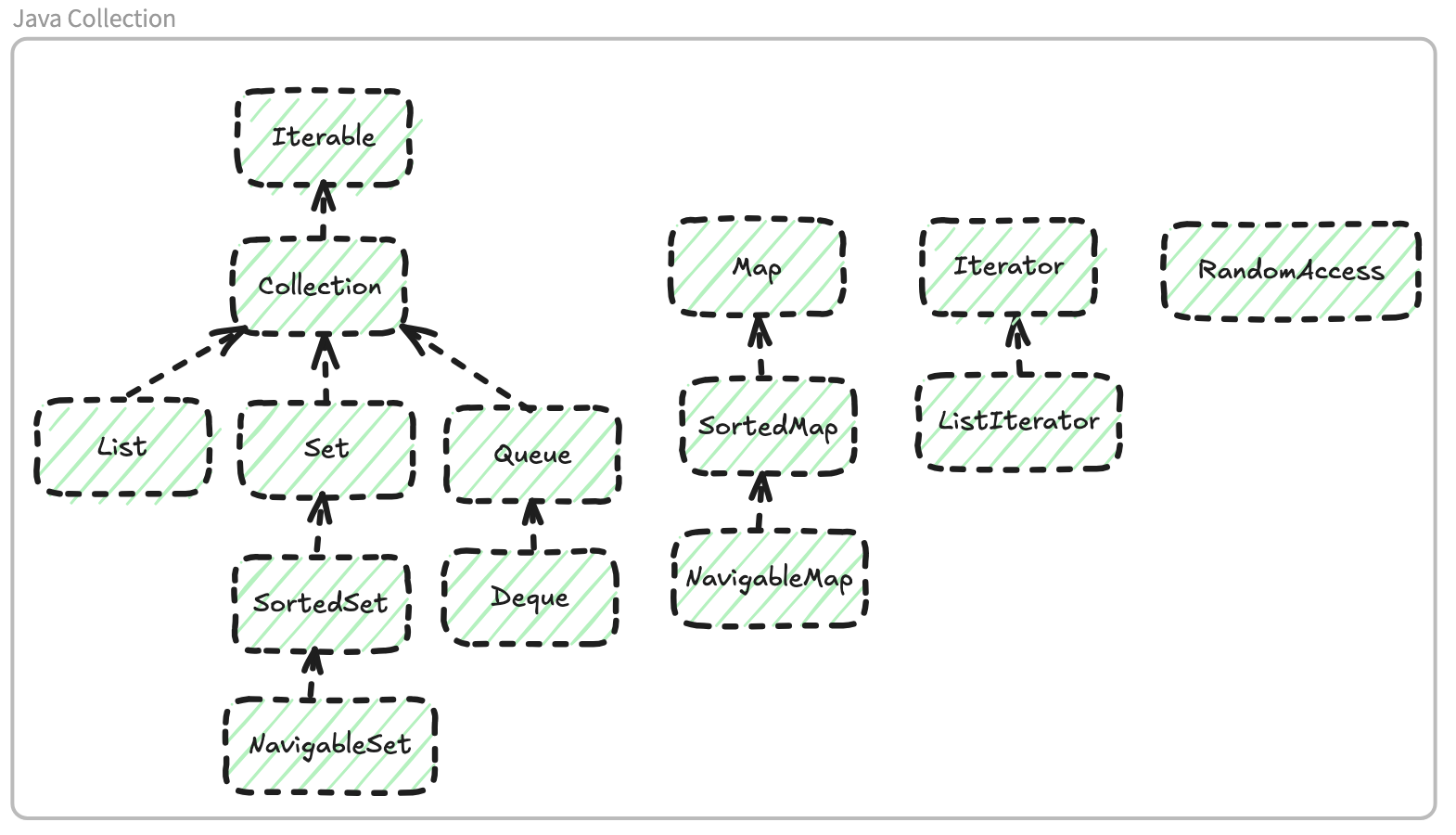
Collection Interface
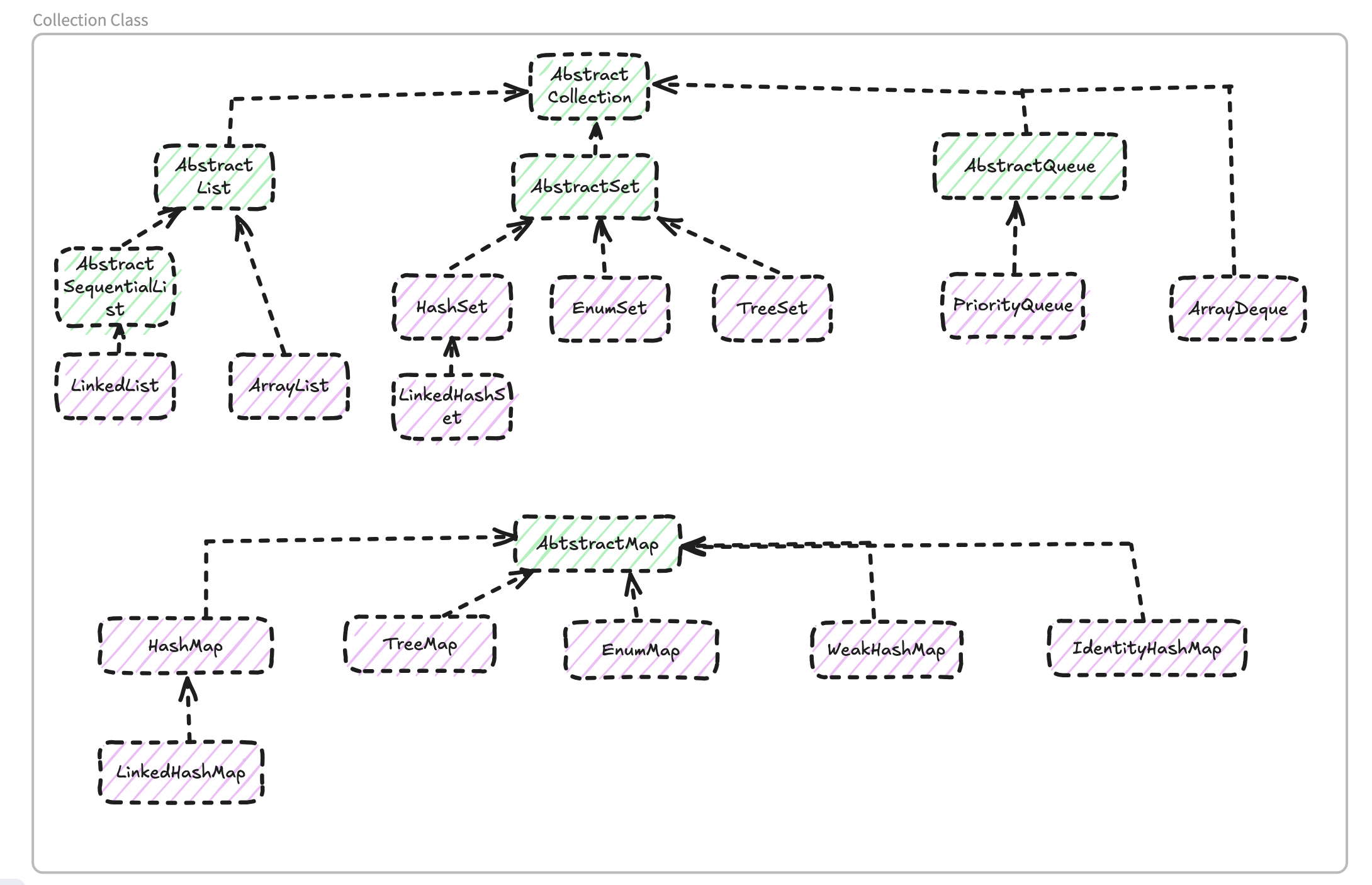
Collection Class
- HashSet in Java - calculate hashcode - hashcode%buck_num to get which bucket to put item in - if buck already has item, then make it as a link list - bucket number: usually 75% to 150% of total item number - load factor: when to rehash hashtable, usually 0.75, which means rehash table if 75% of buckets are already full - TreeSet - A sorted set using red-black tree algorithm - WeakHashMap: WeakHashMap use weak reference to store key. For java GC, if a object is only referred by a weak refernce, then it will be collected and put into a special queue. WeakHashMao will check items put in the queue periodically and remove them from map. This is to solve the issue that for hashmap, value object can never be removed by GC if key is not existing anymore. - EnumSet uses bit to represent value in the set, because number of items should always be infinite. - IdentityHashMap uses System.identityHashCode to calculate hashcode, this will check the memory address of an object, which means different object will have different hashcode even if they have exactly same attributes.Chapter 12 - Concurrency
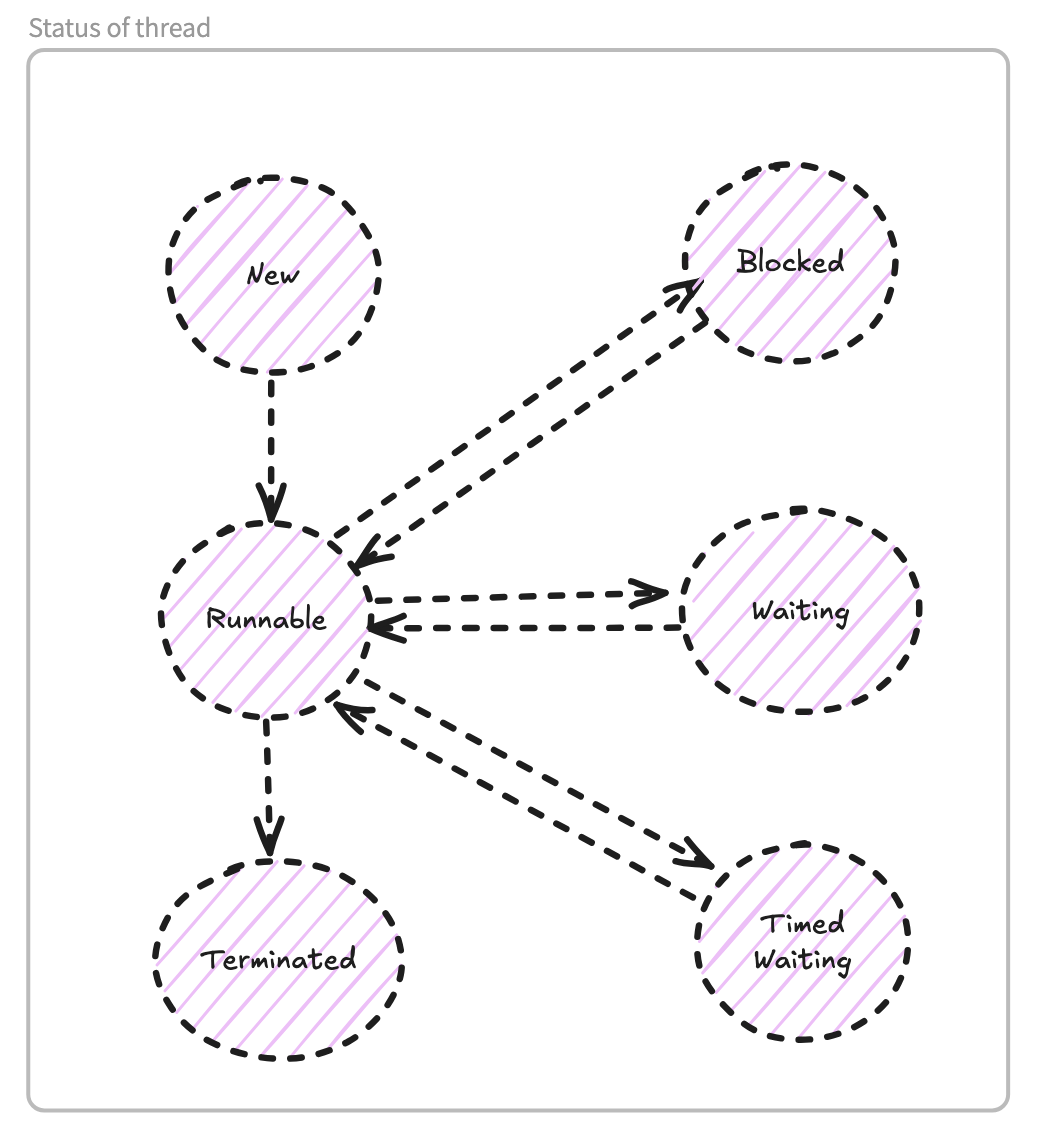
Status of thread
-
interrupt(): send an interrupt request to a thread, it will set interrupt property to true. If this thread is blocked or sleeping, it will throw InterruptedException.
-
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler
- If current thread has a parent thread group, call uncaughtException method of parent group.
- If Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler returns a non-null handler, invoke that handler.
- If Throwable is a instance of ThreadDeath, do nothing.
- Print name of the thraed to stack trace using System.err.
-
Synchronization
- ReentrantLock()
- Condition:
class Bank{ private Condition sufficientFunds; public Bank() { sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition(); } public void transfer() { bankLock.lock(); try { if (amount < 100) { sufficientFunds.await(); } transferMoney(); sufficientFunds.signalAll(); } finally { bankLock.unlock(); } } }- synchronized
synchronized(obj) { doActionA(); doActionB(): }- Blocking Queue
- ConcurrentHashMap, ConcurrentSkipListMap, ConcurrentSkipListSet, ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- CopyOnWriteArrayList, CopyOnWriteArraySet
- Arrays.parallelSort(), Arrays.parallelSetAll()
- ExecutorService: create thread pool
- Async calc: CompletableFuture
